The Leipzig score for Wilson’s disease is a diagnostic tool that combines various clinical, biochemical, and genetic criteria to assess the likelihood of the disease. This scoring system was developed at the 8th International Meeting on Wilson’s Disease in Leipzig in 2001 and has been incorporated into clinical practice guidelines by the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL).
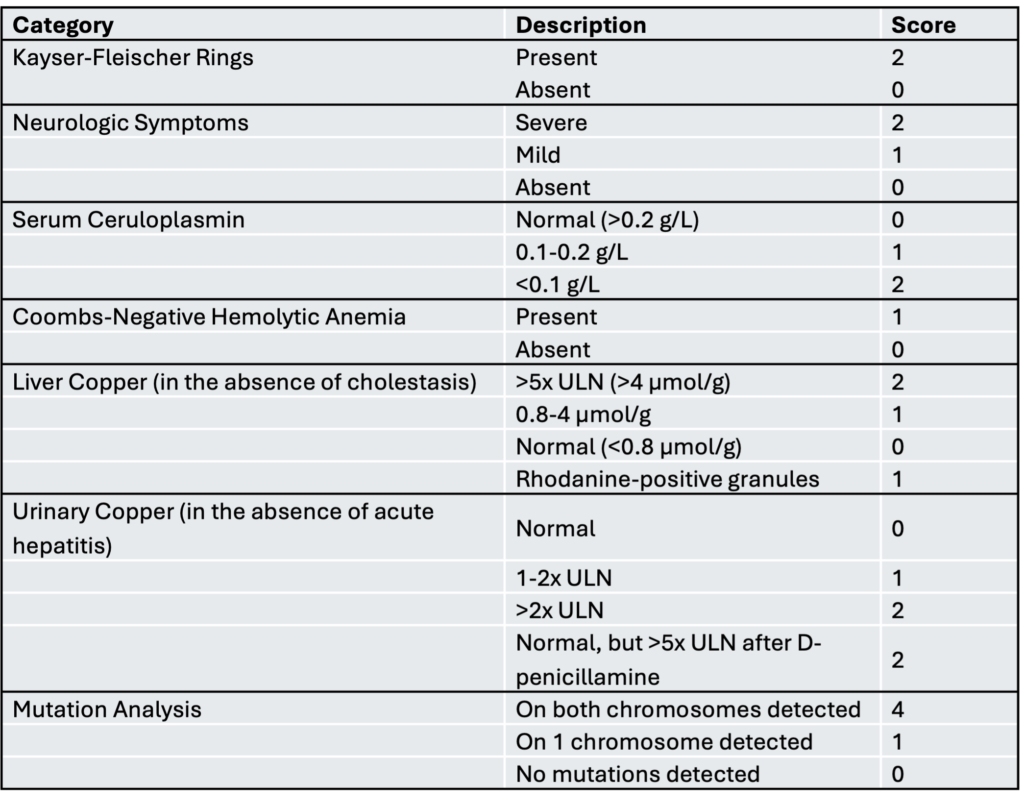
As a table to copy-paste in word
| Category | Description | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Kayser-Fleischer Rings | Present | 2 |
| Absent | 0 | |
| Neurologic Symptoms | Severe | 2 |
| Mild | 1 | |
| Absent | 0 | |
| Serum Ceruloplasmin | Normal (>0.2 g/L) | 0 |
| 0.1-0.2 g/L | 1 | |
| <0.1 g/L | 2 | |
| Coombs-Negative Hemolytic Anemia | Present | 1 |
| Absent | 0 | |
| Liver Copper (in the absence of cholestasis) | >5x ULN (>4 μmol/g) | 2 |
| 0.8-4 μmol/g | 1 | |
| Normal (<0.8 μmol/g) | 0 | |
| Rhodanine-positive granules | 1 | |
| Urinary Copper (in the absence of acute hepatitis) | Normal | 0 |
| 1-2x ULN | 1 | |
| >2x ULN | 2 | |
| Normal, but >5x ULN after D-penicillamine | 2 | |
| Mutation Analysis | On both chromosomes detected | 4 |
| On 1 chromosome detected | 1 | |
| No mutations detected | 0 |
A score of 4 or more confirms the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease. A score of 3 indicates that the diagnosis is possible but requires further testing, while a score of 2 or lower suggests that Wilson’s disease is unlikely
References: